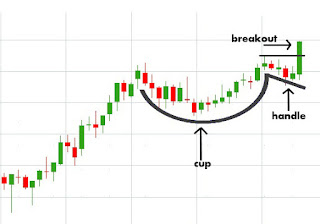
The Cup with Handle is a bullish continuation pattern that marks a consolidation period followed by a breakout. It was developed by William O'Neil and introduced in his 1988 book, How to Make Money in Stocks.
As its name implies, there are two parts to the pattern: the cup and the handle. The cup forms after an advance and looks like a bowl or rounding bottom. As the cup is completed, a trading range develops on the right hand side and the handle is formed. A subsequent breakout from the handle's trading range signals a continuation of the prior advance.
Trend: To qualify as a continuation pattern, a prior trend should exist. Ideally, the trend should be a few months old and not too mature. The more mature the trend, the less chance that the pattern marks a continuation or the less upside potential.
Cup: The cup should be "U" shaped and resemble a bowl or rounding bottom. A "V" shaped bottom would be considered too sharp of a reversal to qualify. The softer "U" shape ensures that the cup is a consolidation pattern with valid support at the bottom of the "U". The perfect pattern would have equal highs on both sides of the cup, but this is not always the case.
Cup Depth: Ideally, the depth of the cup should retrace 1/3 or less of the previous advance. However, with volatile markets and over-reactions, the retracement could range from 1/3 to 1/2. In extreme situations, the maximum retracement could be 2/3, which is conforms with Dow Theory.
Handle: After the high forms on the right side of the cup, there is a pullback that forms the handle. Sometimes this handle resembles a flag or pennant that slopes downward, other times just a short pullback. The handle represents the final consolidation/pullback before the big breakout and can retrace up to 1/3 of the cup's advance, but usually not more. The smaller the retracement is, the more bullish the formation and significant the breakout. Sometimes it is prudent to wait for a break above the resistance line established by the highs of the cup.
Duration: The cup can extend from 1 to 6 months, sometimes longer on weekly charts. The handle can be from 1 week to many weeks and ideally completes within 1-4 weeks.
Target: The projected advance after breakout can be estimated by measuring the distance from the right peak of the cup to the bottom of the cup.